Abstract
Background: Sof Umer Cave is a unique habitat that hosts industrially significant microbes. In this study, Stenotrophomonas sp. ASucR1 was isolated from the cave rock and screened for antimicrobial activity. High-molecular-weight genomic DNA was extracted and subjected to whole-genome sequencing using the Illumina NovaSeq platform. Comprehensive genomic and biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) profiling was conducted.
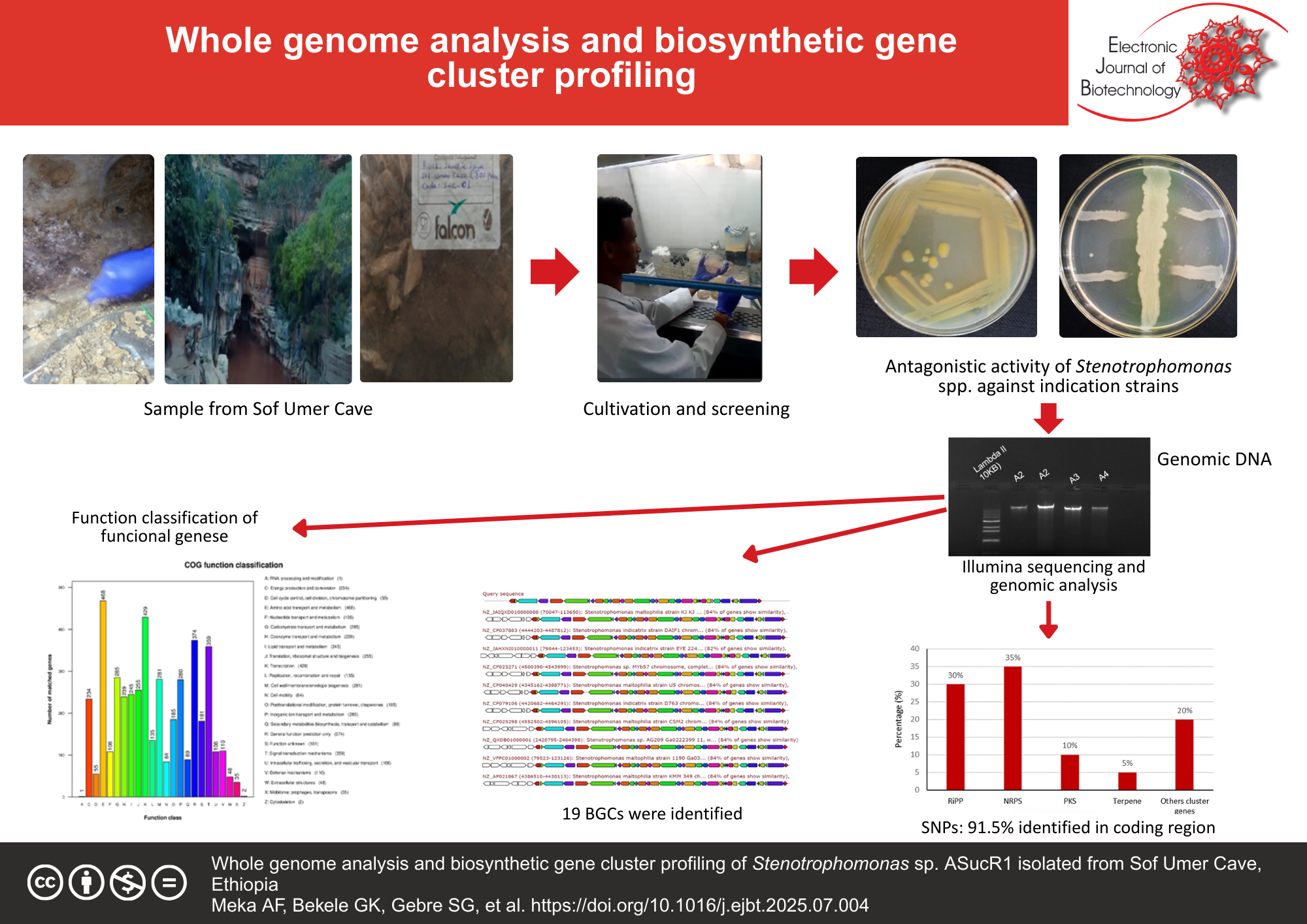
Results: In vitro tests revealed that Stenotrophomonas sp. ASucR1 exhibited a broad spectrum of antagonistic activity. Functional genome annotation identified diverse biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) and metabolic pathways, including genes involved in the synthesis of secondary metabolites. A total of 19 BGCs were identified, several of which showed no matches in the minimum information about a biosynthetic gene cluster (MiBIG) database, indicating the presence of previously uncharacterized bioactive compounds. Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis showed that 91.5% of variants were identified within coding regions, with 85.84% being synonymous. Classification of SNPs and insertion-deletion mutations through clusters of orthologous groups (COG) analysis highlighted their association with key biological functions.
Conclusions: This study highlights the metabolic versatility and biosynthetic potential of Stenotrophomonas sp. ASucR1, a promising candidate for antimicrobial development and biotechnological applications. The identification of various biosynthetic gene clusters paves the way for exploring bioactive compounds with pharmaceutical significance.
References
. Cyske Z, Jaroszewicz W, ?abi?ska M, et al. Unexplored potential: Biologically active compounds produced by microorganisms from hard-to-reach environments and their applications. Acta Biochim Pol 2021;68(4):565-574. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2020_5887 PMid: 34536268
. Meka AF, Bekele GK, Abas MK, et al. Exploring microbial diversity and functional gene dynamics associated with the microbiome of Sof Umer cave, Ethiopia. Discov Appl Sci 2024;6:400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-024-06110-x
. Khatri A, Kumar K, Thakur IS. Microbiome of caves for bioprospecting: a critical review. Syst Microbiol Biomanuf 2025;5:550-566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-024-00322-3
. Samanta B, Sharma S, Budhwar R. Metagenome analysis of speleothem microbiome from subterranean cave reveals insight into community structure, metabolic potential, and BGCs diversity. Curr Microbiol 2023;80:317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03431-9 PMid: 37561193
. Meka AF, Bekele GK, Abas MK, et al. Exploring bioactive compound origins: Profiling gene cluster signatures related to biosynthesis in microbiomes of Sof Umer Cave, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2025;20(3):e0315536. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0315536 PMid: 40048434
. Mukherjee P, Roy P. Genomic potential of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in bioremediation with an assessment of its multifaceted role in our environment. Front Microbiol 2016;7:967. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00967
. Brooke JS. Advances in the microbiology of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Clin Microbiol Rev 2021;34(3):e00030-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00030-19 PMid: 34043457
. Farooq A, Kanwal R, Bashir K, et al. Multi-omics analysis of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia S-11 reveals its potential for Pb²? bioremediation in contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 2025;495:138867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.138867 PMid: 40499424
. Ryan R, Monchy S, Cardinale M, et al. The versatility and adaptation of bacteria from the genus Stenotrophomonas. Nat Rev Microbiol 2009;7:514–525. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2163 PMid: 19528958
. Pandey A, Israr J, Pandey J, et al. Current approaches and implications in discovery of novel bioactive products from microbial sources. Curr Microbiol 2025;82:258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-025-04237-7 PMid: 40263159
. Blin K, Shaw S, Augustijn HE, et al. antiSMASH 7: new features for the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 2023;51(W1):W46–W50. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad344 PMid: 37140036
. Seemann T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014;30(14):2068–2069. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153 PMid: 24642063.
. Lin H, Yu M, Wang X, et al. Comparative genomic analysis reveals the evolution and environmental adaptation strategies of vibrios. BMC Genomics 2018;19:135. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4531-2 PMid: 29433445
. Utturkar S, Dassanayake A, Nagaraju S, et al. Bacterial differential expression analysis methods. In: Himmel M, Bomble Y, eds. Metabolic Pathway Engineering. Methods Mol Biol 2020;2096:135-151. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0195-2_8 PMid: 32720149
. Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014;30(15):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170 PMid: 24695404
. Prjibelski A, Antipov D, Meleshko D, et al. Using SPAdes De Novo Assembler. Curr Protoc Bioinform 2020;70(1):e102. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.102 PMid: 32559359
. Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, et al. QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013;29(8):1072–1075. https://doi.org/10.093/bioinformatics/btt086 PMid: 23422339
. Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT, et al. CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res 2015;25:1043–1055. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.186072.114 PMid: 25977477
. Yao Z, You FM, N’Diaye A et al. Evaluation of variant calling tools for large plant genome re-sequencing. BMC Bioinformatics 2020;21:360. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-020-03704-1 PMid: 32807073
. Danecek P, Bonfield JK, Liddle J, et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021;10(2):giab008. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giab008 PMid: 33590861
. Quinlan AR. BEDTools: the Swiss-army tool for genome feature analysis. Curr Protoc Bioinform 2014;47(1):11.12.1–11.12.34. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi1112s47 PMid: 25199790
. Saleh AA, Xue L, Zhao Y. Screening Indels from the whole genome to identify the candidates and their association with economic traits in several goat breeds. Funct Integr Genomics 2023;23:58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-00981-w PMid: 36757519
. Cingolani P. Variant annotation and functional prediction: SnpEff. In: Ng C, Piscuoglio S, eds. Variant Calling. Methods Mol Biol 2022;2493:289–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2293-3_19 PMid: 35751823
. Karunakaran C, Niranjan V, Setlur AS, et al. Exploring the role of non-synonymous and deleterious variants identified in colorectal cancer: A multi-dimensional computational scrutiny of exomes. Curr Genomics 2024;25(1):41–64. https://doi.org/10.2174/0113892029285310231227105503 PMid: 38544823
. Zada S, Sajjad W, Rafiq M, et al. Cave microbes as a potential source of drugs development in the modern era. Microb Ecol 2022;84:676–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-021-01889-3 PMid: 34693460
. Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, et al. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005;21(18):3674–3676. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610 PMid: 16081474
. Kanehisa M, Sato Y. KEGG Mapper for inferring cellular functions from protein sequences. Protein Sci 2020;29(1):28–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3711 PMid: 31423653
. Cantalapiedra CP, Hernández-Plaza A, Letunic I, et al. eggNOG-mapper v2: Functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. Mol Biol Evol 2021;38(12):5825–5829. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab293 PMid: 34597405
. Galperin MY, Wolf YI, Makarova KS, et al. COG database update: Focus on microbial diversity, model organisms, and widespread pathogens. Nucleic Acids Res 2021;49(D1):D274–D281. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1018 PMid: 33167031
. Stevenson KJ. Review of OriginPro 8.5. J Am Chem Soc 2011;133(14):5621. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja202216h
. Gatinho P, Salvador C, Gutierrez-Patricio S, et al. From cultural and natural heritage to reservoir of biomedicine: Prospection of bioactive compounds produced by bacterial isolates from caves. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 2024;190:105773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2024.105773
. Pipite A, Lockhart PJ, McLenachan PA, et al. Isolation, antibacterial screening, and identification of bioactive cave dwelling bacteria in Fiji. Front Microbiol 2022;13:1012867. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1012867 PMid: 36605510
. Obrador-Sanchez JA, Tzec-Sima M, Higuera-Ciapara I, et al. A quick and effective in-house method of DNA purification from agarose gel, suitable for sequencing. 3 Biotech 2017;7:180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0851-1 PMid: 28664367
. Narzisi G, Mishra B. Comparing de novo genome assembly: The long and short of it. PLoS ONE 2011;6(4):e19175. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019175 PMid: 21559467
. Chklovski A, Parks DH, Woodcroft BJ, et al. CheckM2: a rapid, scalable and accurate tool for assessing microbial genome quality using machine learning. Nat Methods 2023;20:1203–1212. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-023-01940-w PMid: 37500759
. Krishnamurthy HK, Rajavelu I, Pereira M, et al. Inside the genome: understanding genetic influences on oxidative stress. Front Genet 2024;15:1397352. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2024.1397352 PMid: 38983269
. Zhang J, Qian W. Functional synonymous mutations and their evolutionary consequences. Nat Rev Genet 2025. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-025-00850-1
. Terlouw BR, Blin K, Navarro-Muñoz JC, et al. MIBiG 3.0: a community-driven effort to annotate experimentally validated biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res 2023;51(D1):D603–D610. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1049 PMid: 36399496
. Blin K, Kim HU, Medema MH, et al. Recent development of antiSMASH and other computational approaches to mine secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters. Brief Bioinform 2019;20(4):1103–1113. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx146 PMid: 29112695
. Zhao Y, Ding WJ, Xu L, et al. A comprehensive comparative genomic analysis revealed that plant growth promoting traits are ubiquitous in strains of Stenotrophomonas. Front Microbiol 2024;15:1395477. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1395477 PMid: 38817968
. Ulrich K, Kube M, Becker R, et al. Genomic analysis of the endophytic Stenotrophomonas strain 169 reveals features related to plant-growth promotion and stress tolerance. Front Microbiol 2021;12:687463. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.687463 PMid: 34220780
. Ercole TG, Kava VM, Petters-Vandresen DAL, et al. Unveiling agricultural biotechnological prospects: The draft genome sequence of Stenotrophomonas geniculata LGMB417. Curr Microbiol 2024;81:247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-024-03784-9 PMid: 38951210
. Galià-Camps C, Pegueroles C, Turon X, et al. Genome composition and GC content influence loci distribution in reduced representation genomic studies. BMC Genomics 2024;25:410. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-024-10312-3 PMid: 38664648
. Hu EZ, Lan XR, Liu ZL, et al. A positive correlation between GC content and growth temperature in prokaryotes. BMC Genomics 2022;23:110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08353-7 PMid: 35139824
. Sarkar D, Nanda S, Poddar K, et al. Isolation and characterization of an antibacterial compound producing Stenotrophomonas strain from sewage water, production optimization, and its antibiotic potential evaluation. Environ Qual Manag 2022;31 (4):51–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/tqem.21764

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2025 Electronic Journal of Biotechnology