Abstract
Background: Alkaline stress severely restricts rice growth and yield by disrupting ion balance, nutrient uptake, and oxidative metabolism. Clarifying the molecular mechanisms of tolerance is vital for breeding resilient varieties. This study explores transcriptional and metabolic adaptations in an alkali-tolerant (Qijing 10, LD) and sensitive (Tengxi 138, WL) rice variety under alkaline stress.
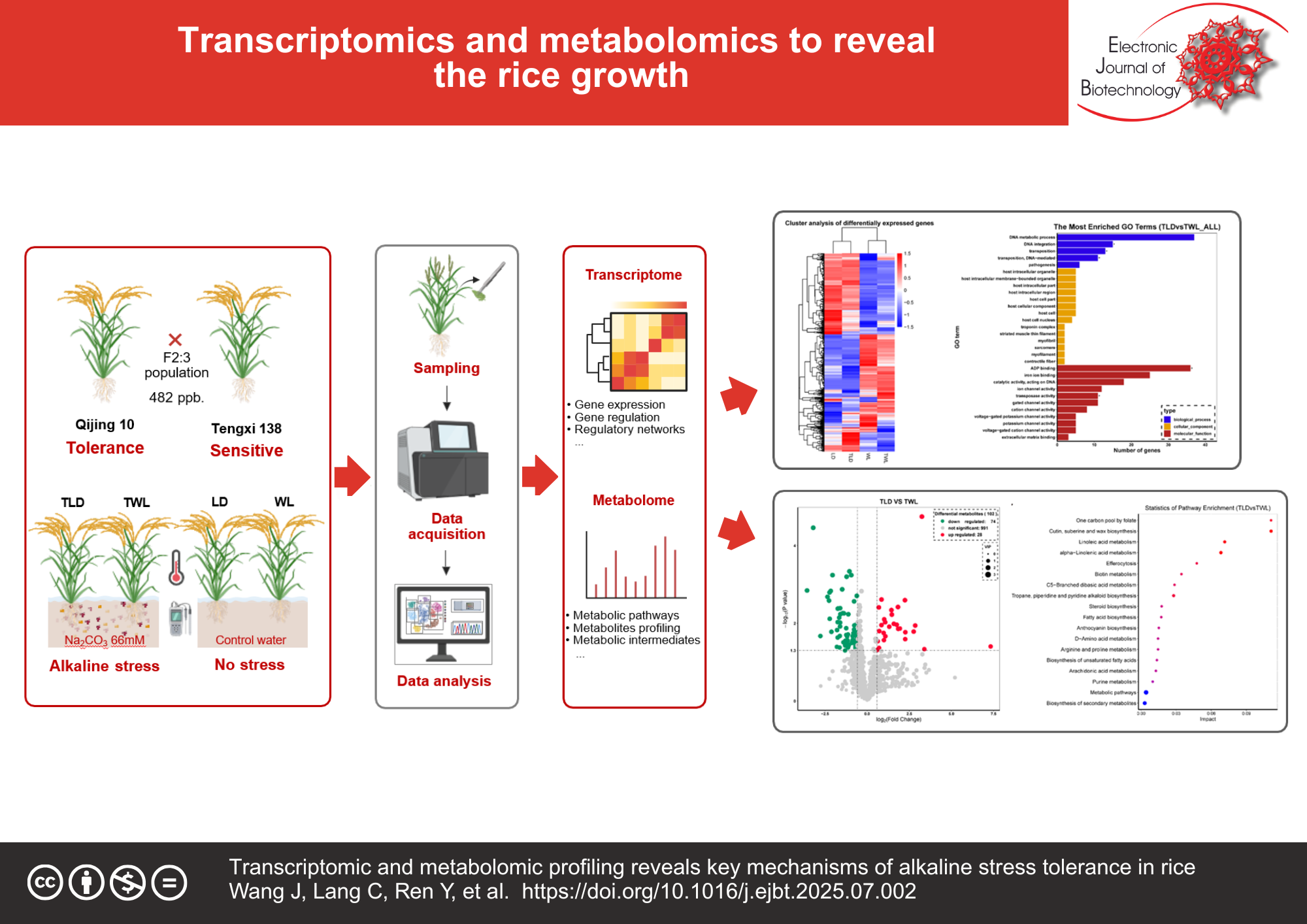
Results: Transcriptomic analysis revealed 1297 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the sensitive variety under alkaline stress (TWL), primarily enriched in pathways related to antioxidant enzyme synthesis (e.g., peroxidase genes), transmembrane ion transport, and membrane lipid stabilization pathways. In contrast, the tolerant variety (TLD) exhibited only 38 DEGs, suggesting transcriptional homeostasis achieved via suppression of stress-related gene overactivation. Metabolomic profiling demonstrated stable levels of key lipids (phosphatidic acid, galactolipids) and osmolytes (proline, betaine) in the tolerant variety under stress, whereas the sensitive variety accumulated lipid peroxidation products (malondialdehyde, MDA) and displayed dysregulated carbohydrate metabolic dysregulation. Integrated multi-omics analysis indicated that the tolerant variety coordinated lipid metabolism gene modulation with antioxidant metabolite accumulation, establishing dual barriers for ROS scavenging and membrane protection. Conversely, transcriptional dysregulation in the sensitive variety led to metabolic collapse.
Conclusions: Alkaline tolerance in rice hinges on the synergistic modulation of stress-responsive genes and metabolic networks to preserve redox equilibrium and membrane function. The tolerant variety’s capacity to stabilize transcriptional activity and metabolic flux underlies its resilience. These results elucidate key molecular and metabolic determinants of alkaline tolerance, offering strategic targets for breeding rice cultivars adapted to alkaline environments.
References
Zhang, H., Yu, F., Xie, P., et al. A G? protein regulates alkaline sensitivity in crops. Science 2023;379(6638):eade8416. https://10.1126/science.ade8416 PMid: 36952416
Kaiwen, G., Zisong, X., Yuze, H., et al. Effects of salt concentration, pH, and their interaction on plant growth, nutrient uptake, and photochemistry of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) leaves. Plant Signal Behav 2020;15(12):1832373. https://10.1080/15592324.2020.1832373 PMid: 33073686
Zhang, H., Liu, X.L., Zhang, R.X., et al. Root damage under alkaline stress is associated with reactive oxygen species accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front Plant Sci 2017;8:1580. https://10.3389/fpls.2017.01580 PMid: 28943882
Fang, S., Hou, X., Liang, X. Response mechanisms of plants under saline-alkali stress. Front Plant Sci 2021;12:667458. https://10.3389/fpls.2021.667458 PMid: 34149764
Yu, J., Li, Y., Qin, Z., et al. Plant chloroplast stress response: insights from Thiol Redox Proteomics. Antioxid Redox Signal 2020;33(1):35-57. https://10.1089/ars.2019.7823 PMid: 31989831
Cao, Y., Song, H., Zhang, L. New insight into plant saline-alkali tolerance mechanisms and application to breeding. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23(24):16048. https://10.3390/ijms232416048 PMid: 36555693
Fan, C. Genetic mechanisms of salt stress responses in halophytes. Plant Signal Behav 2020;15(1):1704528. https://10.1080/15592324.2019.1704528 PMid: 31868075
Yu, X., Liu, Z., Sun, X. Single-cell and spatial multi-omics in the plant sciences: Technical advances, applications, and perspectives. Plant Commun 2023;4(3):100508. https://10.1016/j.xplc.2022.100508 PMid: 36540021
Feng, Z., Ding, C., Li, W., et al. Applications of metabolomics in the research of soybean plant under abiotic stress. Food Chem 2020;310:125914. https://10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125914 PMid: 31835223
Seyfferth, C., Renema, J., Wendrich, J.R., et al. Advances and opportunities in single-cell transcriptomics for plant research. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2021;72:847-866. https://10.1146/annurev-arplant-081720-010120 PMid: 33730513
Allwood, J.W., Williams, A., Uthe, H., et al. Unravelling plant responses to stress-the importance of targeted and untargeted metabolomics. Metabolites 2021;11(8):558. https://10.3390/metabo11080558 PMid: 34436499
Yang, Y., Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol 2018;217(2):523-539. https://10.1111/nph.14920 PMid: 29205383
Jorge, T.F., Rodrigues, J.A., Caldana, C., et al. Mass spectrometry-based plant metabolomics: Metabolite responses to abiotic stress. Mass Spectrom Rev 2016;35(5):620-649. https://10.1002/mas.21449 PMid: 25589422
Yan, J., Wang, X. Machine learning bridges omics sciences and plant breeding. Trends Plant Sci 2023;28(2):199-210. https://10.1016/j.tplants.2022.08.018 PMid: 36153276
Zhao, C., Zhang, H., Song, C., et al. Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Innovation 2020;1(1):100017. https://10.1016/j.xinn.2020.100017 PMid: 34557705
Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 2016;167(2):313-324. https://10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.029 PMid: 27716505
Zhang, H., Zhu, J., Gong, Z., et al. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat Rev Genet 2022;23(2):104-119. https://10.1038/s41576-021-00413-0 PMid: 34561623
Danquah, A., de Zelicourt, A., Colcombet, J., et al. The role of ABA and MAPK signaling pathways in plant abiotic stress responses. Biotechnol Adv 2014;32(1):40-52. https://10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.09.006 PMid: 24091291
Xu, X., Zhang, J., Yan, B., et al. The adjustment of membrane lipid metabolism pathways in maize roots under saline-alkaline stress. Front Plant Sci 2021;12:635327. https://10.3389/fpls.2021.635327 PMid: 33790924
Qian, G., Wang, M., Wang, X., et al. Integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis of rice leaves response to high saline-alkali stress. Int J Mol Sci 2023;24(4):4062. https://10.3390/ijms24044062 PMid: 36835473
Sagervanshi, A., Geilfus, C.M., Kaiser, H., et al. Alkali salt stress causes fast leaf apoplastic alkalinization together with shifts in ion and metabolite composition and transcription of key genes during the early adaptive response of Vicia faba L. Plant Sci 2022;319:111253. https://10.1016/j.plantsci.2022.111253 PMid: 35487662
Ma, S., Lv, L., Meng, C., et al. Integrative analysis of the metabolome and transcriptome of Sorghum bicolor reveals dynamic changes in flavonoids accumulation under saline-alkali stress. J Agric Food Chem 2020;68(50):14781-14789. https://10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06249 PMid: 33274637
Zhang, Z., Zhang, F., Deng, Y., et al. Integrated metabolomics and transcriptomics analyses reveal the metabolic differences and molecular basis of nutritional quality in landraces and cultivated rice. Metabolites 2022;12(5):384. https://10.3390/metabo12050384 PMid: 35629888
Hara, Y., Tatsumi, K., Yoshida, M., et al. Optimizing and benchmarking de novo transcriptome sequencing: from library preparation to assembly evaluation. BMC Genomics 2015;16:977. https://10.1186/s12864-015-2007-1 PMid: 26581708
Hrdlickova, R., Toloue, M., Tian, B. RNA-Seq methods for transcriptome analysis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2017;8(1):e1364. https://10.1002/wrna.1364 PMid: 27198714
Wang, Z., Gerstein, M., Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 2009;10 (1):57-63. https://10.1038/nrg2484 PMid: 19015660
Trapnell, C., Roberts, A., Goff, L., et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 2012;7(3):562-578. https://10.1038/nprot.2012.016 PMid: 22383036
Marquez, Y., Brown, J.W., Simpson, C., et al. Transcriptome survey reveals increased complexity of the alternative splicing landscape in Arabidopsis. Genome Res 2012;22(6):1184-1195. https://10.1101/gr.134106.111 PMid: 22391557
Volpi, N., Galeotti, F., Gatto, F. High-throughput glycosaminoglycan extraction and UHPLC-MS/MS quantification in human biofluids. Nat Protoc 2024;20:843-860. https://10.1038/s41596-024-01078-9 PMid: 39543382
Han, K., Hua, J., Zhang, Q., et al. Multi-residue analysis of fipronil and its metabolites in eggs by SinChERS-Based UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Sci Anim Resour 2021;41(1):59-70. https://10.5851/kosfa.2020.e76 PMid: 33506217
Chong, J., Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR: an R package for flexible and reproducible analysis of metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2018;34(24):4313-4314. https://10.1093/bioinformatics/bty528 PMid: 29955821
Tautenhahn, R., Cho, K., Uritboonthai, W., et al. An accelerated workflow for untargeted metabolomics using the METLIN database. Nat Biotechnol 2012;30(9):826-828. https://10.1038/nbt.2348 PMid: 22965049
Boccard, J., Rutledge, D.N. A consensus orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) strategy for multiblock Omics data fusion. Anal Chim Acta 2013;769:30-39. https://10.1016/j.aca.2013.01.022 PMid: 23498118
Huang, Y., Sun, Z., Zhou, X. WRKY Transcription factors in response to metal stress in plants: A review. Int J Mol Sci 2024;25(20):10952. https://10.3390/ijms252010952 PMid: 39456735
Li, S., Han, X., Lu, Z., et al. MAPK Cascades and transcriptional factors: regulation of heavy metal tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23(8):4463. https://10.3390/ijms23084463 PMid: 35457281
Maritha, V., Harlina, P.W., Musfiroh, I., et al. The application of chemometrics in metabolomic and lipidomic analysis data presentation for halal authentication of meat products. Molecules 2022;27(21):7571. https://10.3390/molecules27217571 PMid: 36364396
Zhou, Z., Liu, J., Meng, W., et al. Integrated analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals molecular mechanisms of rice with different salinity tolerances. Plants 2023;12(19):3359. https://10.3390/plants12193359 PMid: 37836098
Wang, J., Yan, D., Liu, R., et al. The physiological and molecular mechanisms of exogenous melatonin promote the seed germination of Maize (Zea mays L.) under salt stress. Plants 2024;13(15):2142. https://10.3390/plants13152142 PMid: 39124260
Gechev, T.S., Dinakar, C., Benina, M., et al. Molecular mechanisms of desiccation tolerance in resurrection plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 2012;69(19):3175-3186. https://10.1007/s00018-012-1088-0 PMid: 22833170
Liu, P., Wang, Y., Yang, G., et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids in intestinal barrier function, inflammation, oxidative stress, and colonic carcinogenesis. Pharmacol Res 2021;165:105420. https://10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105420 PMid: 33434620
Yang, J., Zhang, Z., Li, X., et al. A gene cluster for polyamine transport and modification improves salt tolerance in tomato. Plant J 2024;120(5):1706-1723. https://10.1111/tpj.17074 PMid: 39401077
Rizwan, H.M., Shaozhong, F., Li, X., et al. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of KCS gene family in passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) under Fusarium kyushuense and drought stress conditions. Front Plant Sci 2022;13:872263. https://10.3389/fpls.2022.872263 PMid: 35548275
Manna, M., Thakur, T., Chirom, O., et al. Transcription factors as key molecular target to strengthen the drought stress tolerance in plants. Physiol Plant 2021;172(2):847-868. https://10.1111/ppl.13268 PMid: 33180329
Ng, D.W., Abeysinghe, J.K., Kamali, M. Regulating the regulators: The control of transcription factors in plant defense signaling. Int J Mol Sci 2018;19(12):3737. https://10.3390/ijms19123737 PMid: 30477211
Ikram, M., Batool, M., Ullah, M., et al. Molecular alchemy: converting stress into resilience via secondary metabolites and calcium signaling in rice. Rice 2025;18(1):32. https://10.1186/s12284-025-00783-7 PMid: 40325258
Nie, S., Huang, W., He, C., et al. Transcription factor OsMYB2 triggers amino acid transporter OsANT1 expression to regulate rice growth and salt tolerance. Plant Physiol 2025;197(2):kiae559. https://10.1093/plphys/kiae559 PMid: 39425973
Kavi Kishor, P.B., Sreenivasulu, N. Is proline accumulation per se correlated with stress tolerance or is proline homeostasis a more critical issue? Plant Cell Environ 2014;37(2):300-311. https://10.1111/pce.12157 PMid: 23790054
Mattioli, R., Costantino, P., Trovato, M. Proline accumulation in plants: not only stress. Plant Signal Behav 2009;4(11):1016-1018. https://10.4161/psb.4.11.9797 PMid: 20009553
Seo, P.J., Kim, S.G., Park, C.M. Membrane-bound transcription factors in plants. Trends Plant Sci 2008;13(10):550-556. https://10.1016/j.tplants.2008.06.008 PMid: 18722803
Kumar, D., Kirti, P.B. The genus Arachis: an excellent resource for studies on differential gene expression for stress tolerance. Front Plant Sci 2023;14:1275854. https://10.3389/fpls.2023.1275854 PMid: 38023864
Rosenkranz, R.R.E., Ullrich, S., Löchli, K., et al. Relevance and regulation of alternative splicing in plant heat stress response: current understanding and future directions. Front Plant Sci 2022;13:911277. https://10.3389/fpls.2022.911277 PMid: 35812973
Shi, S., Zha, W., Yu, X., et al. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis provide insight into the resistance response of rice against brown planthopper. Front Plant Sci 2023;14:1213257. https://10.3389/fpls.2023.1213257 PMid: 37426975
Zhang, Q., Li, T., Gao, M., et al. Transcriptome and metabolome profiling reveal the resistance mechanisms of rice against brown planthopper. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23(8):4083. https://10.3390/ijms23084083 PMid: 35456901
Liu, L., Li, K., Zhou, X., et al. Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome reveals the role of strigolactones in wounding-induced rice metabolic re-programming. Metabolites 2022;12(9):789. https://10.3390/metabo12090789 PMid: 36144193
Molisso, D., Coppola, M., Buonanno, M., et al. Tomato prosystemin is much more than a simple systemin precursor. Biology 2022;11(1):124. https://10.3390/biology11010124 PMid: 35053122
Li, C., Jia, Y., Zhou, R., et al. GWAS and RNA-seq analysis uncover candidate genes associated with alkaline stress tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. Front Plant Sci 2022;13:963874. https://10.3389/fpls.2022.963874 PMid: 35923879

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2025 Electronic Journal of Biotechnology