Abstract
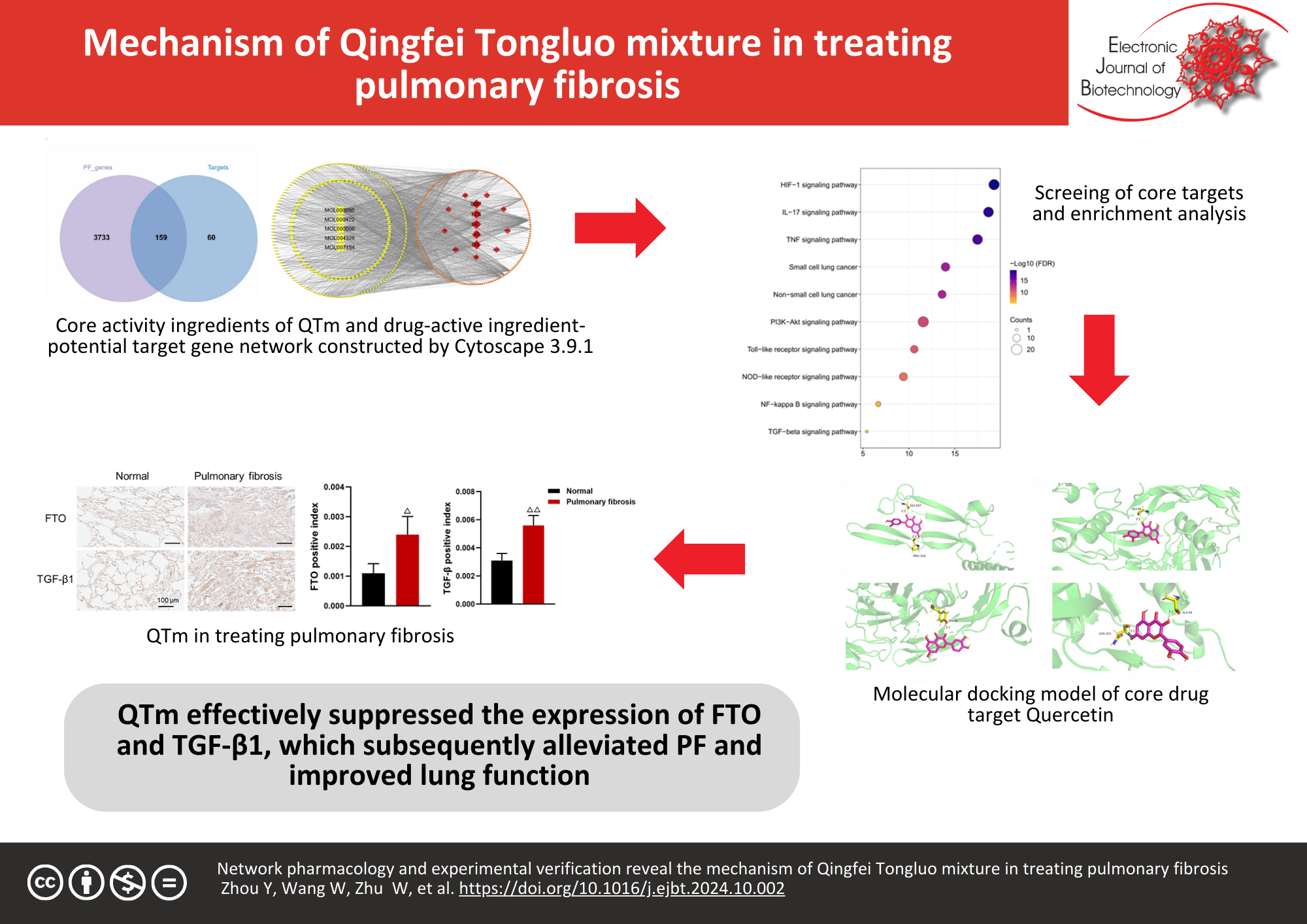
Background: Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a chronic interstitial lung disease posing significant health risks. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic mechanism of Qingfei Tongluo mixture (QTm) in treating PF by combining network pharmacology and experimental verification.
Results: A total of 246 active ingredients in QTm were identified, with 159 potential targets for PF treatment. Quercetin, a key active ingredient, was associated with the TGF-β1 signaling pathway. Gene Ontology and KEGG enrichment analyses identified 42 core genes, with a notable implication of the TGF-beta signaling pathway in PF. Immunohistochemistry showed elevated FTO and TGF-β1 levels in PF tissues. Animal experiments demonstrated that QTm improved alveolar structure, reduced interstitial lesions, and enhanced lung function while decreasing hydroxyproline content and the expression of FTO and TGF-β1 proteins.
Conclusions: QTm may inhibit PF progression by suppressing FTO/TGF-β1 expression, thereby improving lung function. These findings suggest that QTm holds potential as a treatment for PF.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2025 Electronic Journal of Biotechnology